Marie-Agnes SARI
Universite Paris Descartes, France
Title: Antibacterial activity of recombinant and synthetic hepcidin
Biography
Biography: Marie-Agnes SARI
Abstract
Urinary tract infections (UTI), affecting 150 million cases per year worldwide, are the main cause of medical antibiotic prescription. However, uropathogen E. coli (UPEC) responsible for UTI are increasingly resistant to antibiotics, indicating urgent need for new therapeutic alternatives. The goal of our project is to explore hepcidin as a new antimicrobial peptide. Hepcidin is a cysteine rich, β defensin like peptide hormone that acts as the key regulator of body iron metabolism. Hepcidin regulates iron homeostasis in human through the binding of the sole iron exporter protein, ferroportin inducing its internalization prior degradation by lysosomes. Besides the liver that is the major source of bloodstream hepcidin, this peptide is expressed in epithelial barriers that are frequently confronted to pathogen infection, including kidneys. However, hepcidin belongs to defensins family and was observed to have an in vitro antimicrobial activity. We hypothesized that hepcidin was involved in host resistance to UPEC in renal epithelia where iron limit may be efficiently regulated. Hepcidin role against urinary tract infection was investigated using HepC-/-mice and synthetic hepcidin. Several recombinant hepcidins were produced as biologically active, ferroportin-binding peptide in E. coli, or yeast and synthetic hepcidin analogs were prepared and compared for their antibacterial activity on E. coli, B. subtilis and S. aureus. Bacteriostatic activity of hepcidin was demonstrated in vitro on CFT073 (a prototypical pyelonephritis-associated E coli strain). Evidence will be presented demonstrate that hepcidin is an effective mediator against UPEC infection and acts to prevent pathogenesis in the kidney in mice.
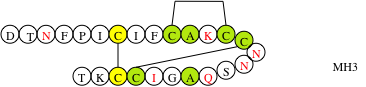
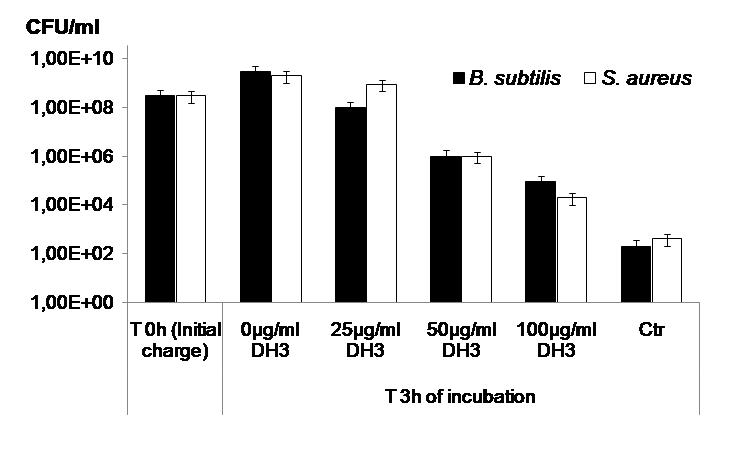
Figure 1: Structure of the mouse hepcidine analog and evaluation of its antimicrobial activity.





